Home
Browsing Animations: Charged Particle Motion
21 Animations
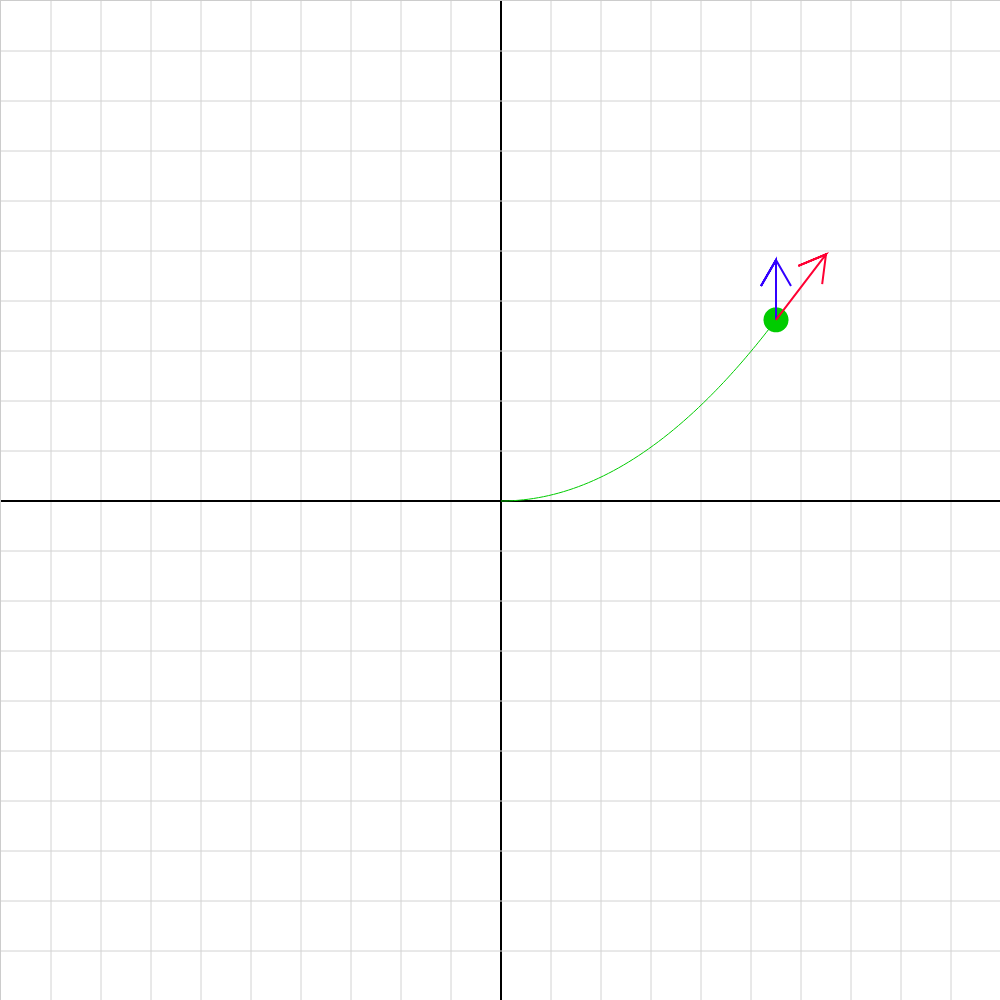
cp-efield-02.iwp
A charged particle moves under the influence of an electric field oriented along the y-axis. Note this sign convention: The direction of positive E is +y (toward top of screen) The red and blue vectors on the particle represents its velocity and acceleration.
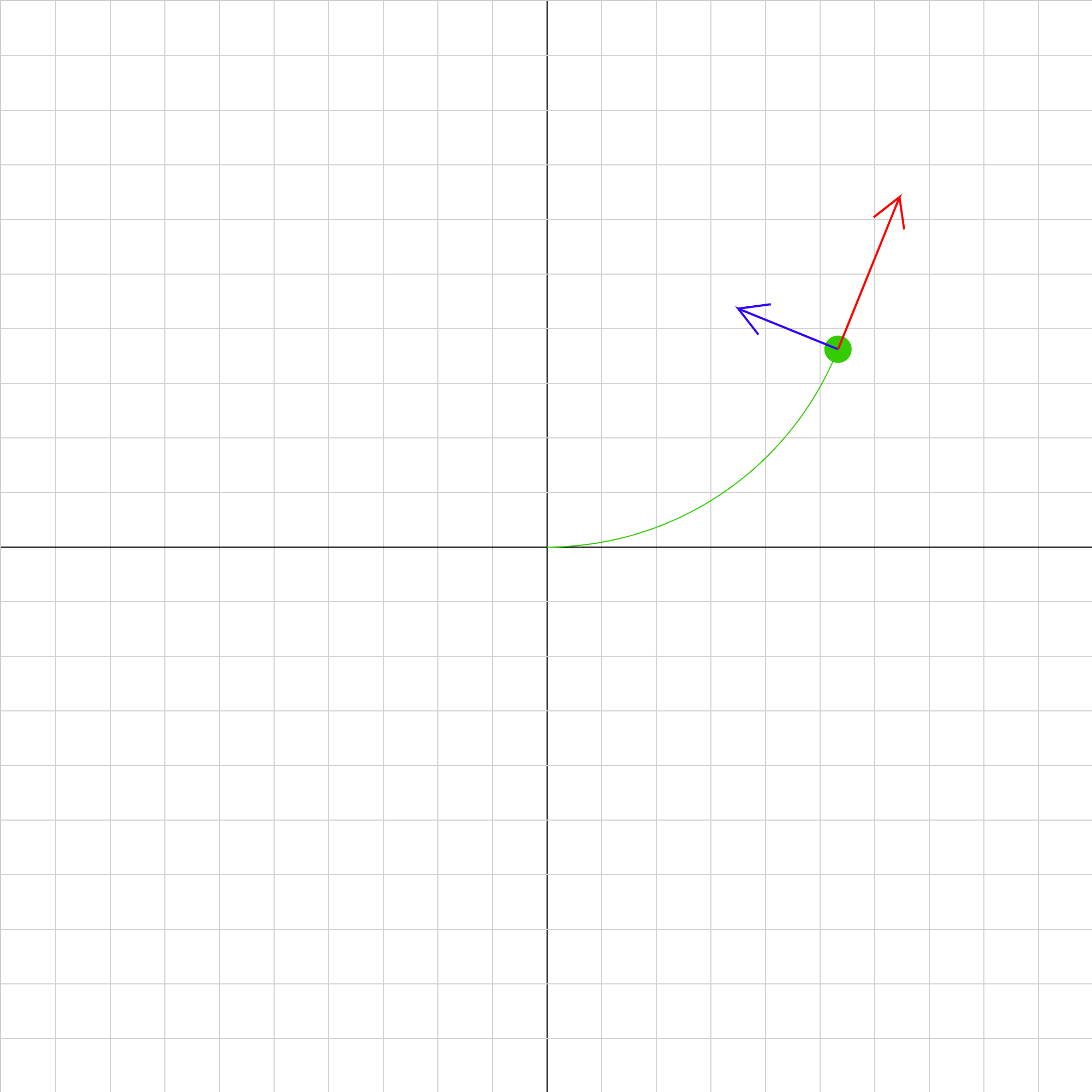
cp-mfield-02.iwp
A charged particle moves under the influence of a magnetic field oriented along the z-axis (perpendicular to the screen). The direction of positive B is +z (outward from screen). The blue vector on the particle represents its acceleration. The grid scale is located under the tab marked by two boxes.
cpchall01.iwp
Challenge 1. An electron is shot along the +y-axis from the origin. Enter the magnetic field that will make the electron move in a path of radius 0.050 m. Note that a positive value of B-field indicates that B points outward from the screen. Also note the following: After making a change in any Input, click Reset. The grid spacing is 0.01 m along both axes. Form of powers of ten entry: 5E-3 = 0.005
cpchall02.iwp
Challenge 2. Orbiting alpha particle An alpha particle is shot along the +y-axis from the origin. Enter the magnetic field that will make the alpha move in a path of radius 0.050 m. Notes: A positive value of B-field indicates that B points outward from the screen. After making a change in any Input, click Reset. The grid spacing is 0.01 m along both axes. Form of powers of ten entry: 5E-3 = 0.005
cpchall03.iwp
Challenge 3. Unknown X particle Use magnetic fields to investigate the unknown X particle. Determine as much as you can about the charge and mass. Notes: A positive value of B-field indicates that B points outward from the screen. After making a change in any Input, click Reset. The grid spacing is 0.01 m along both axes. Form of powers of ten entry: 5E-3 = 0.005
cpchall04.iwp
Challenge 4. Explore electric field Investigate the motion of an electron in an electric field. Compare to the motion in a magnetic field. Try combinations of electric and magnetic fields. Notes: Positive E-fields are to the right and positive B-fields are out of the screen. After making a change in any Input, click Reset. The grid spacing is 0.01 m along both axes. Form of powers of ten entry: 5E-3 = 0.005
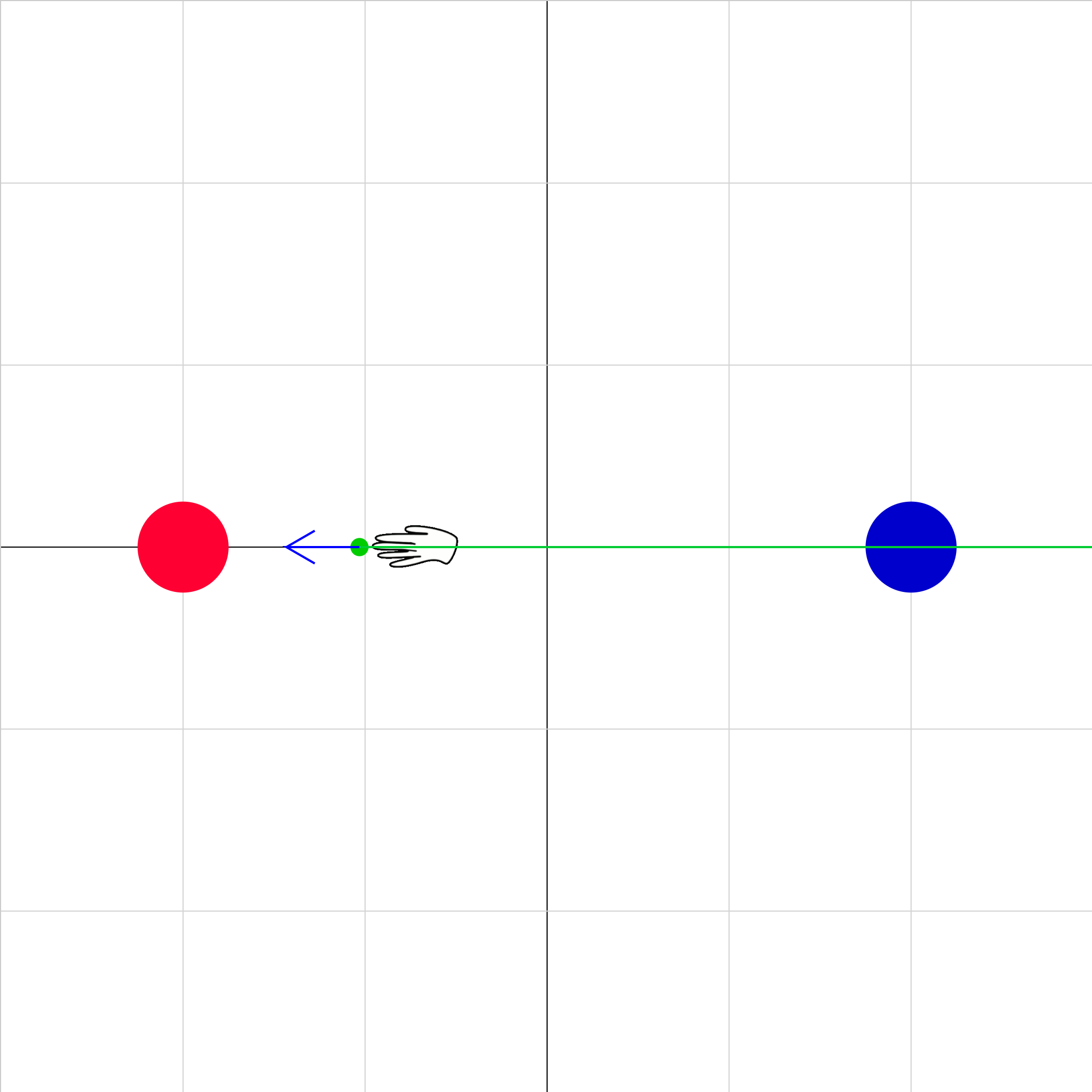
eforce-08.iwp
Two charged objects (red and blue) are fixed in position on the x-axis. When the animation is started, a small green charged object is pushed back and forth between the red and blue objects. (If you want to make the hand invisible, change the Hand Visible input to 0.) The red and blue vectors represent the electric forces on the green object due to red and blue objects respectively. The green vector represents the net electric force on the green object due to the blue and red objects. Step through the animation to see how the net electric force changes with the position of the green object.
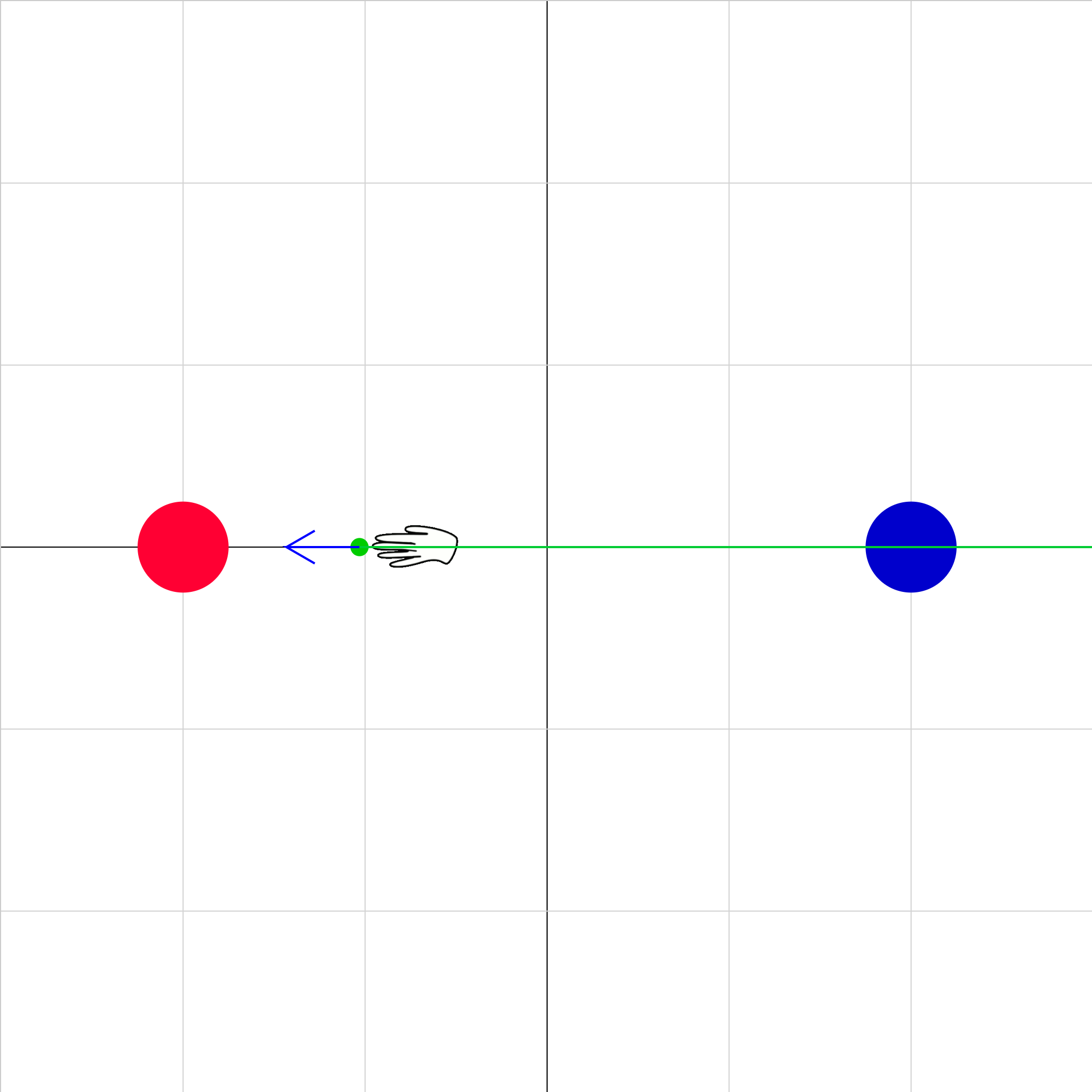
eforce-09.iwp
Two charged objects (red and blue) are fixed in position on the x-axis. When the animation is started, a small green charged object is pushed back and forth between the red and blue objects. (If you want to make the hand invisible, change the Hand Visible input to 0.) The red and blue vectors represent the electric forces on the green object due to red and blue objects respectively. The green vector represents the net electric force on the green object due to the blue and red objects. The position of the green object and magnitude of the net force on the green object are given under Outputs.
em-ratio-1d.iwp
An electron is accelerated from rest under the influence of a potential V1 (not shown). At the origin, the electron enters crossed electric and magnetic fields. The electric field is oriented in the -y direction and is produced by parallel plates with a potential difference equal to V2. The magnetic field is oriented in the -z direction (into screen) and is produced by Helmholtz coils.
em-ratio-2f.iwp
An electron is accelerated from rest and enters an electric field produced by parallel plates with a constant potential difference across them.
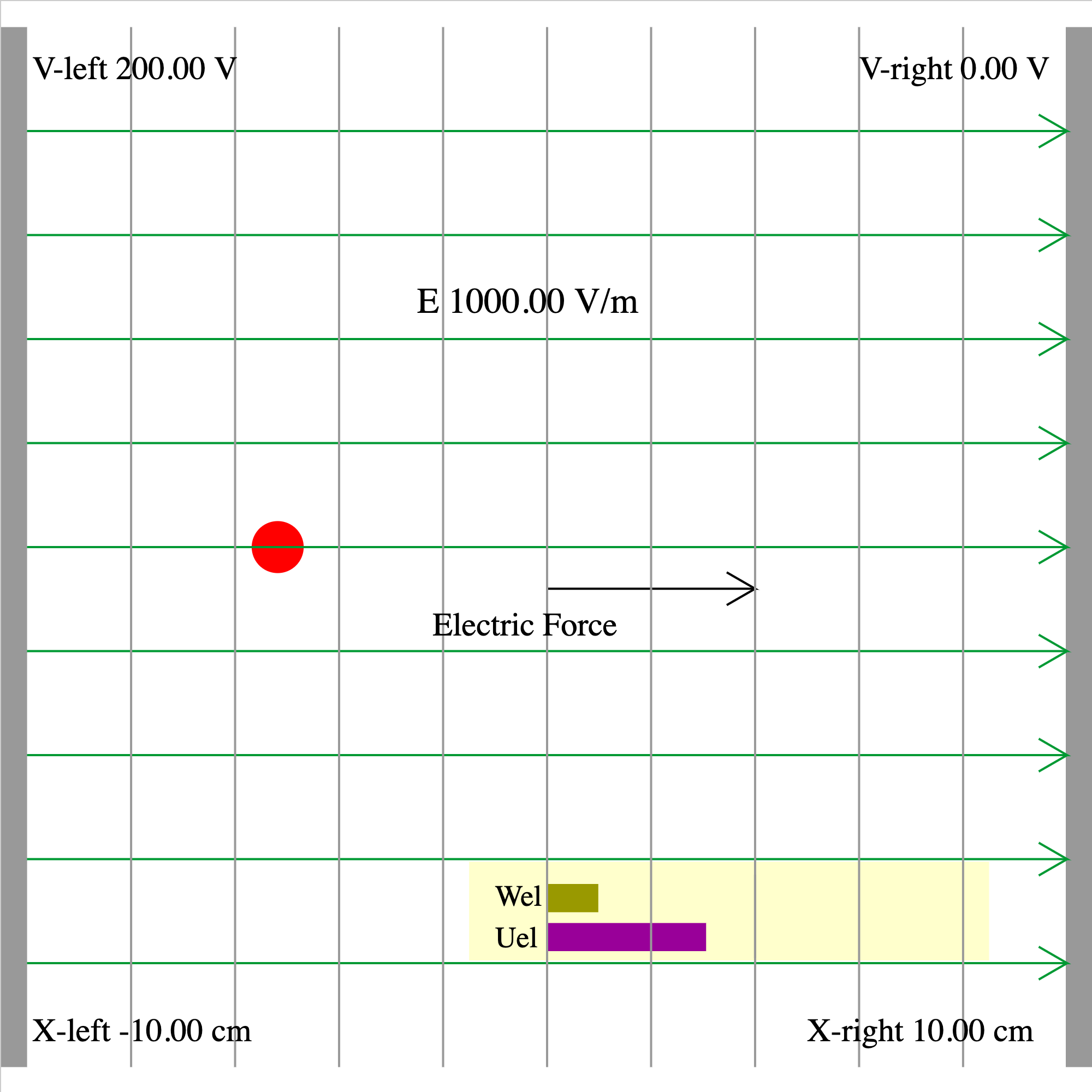
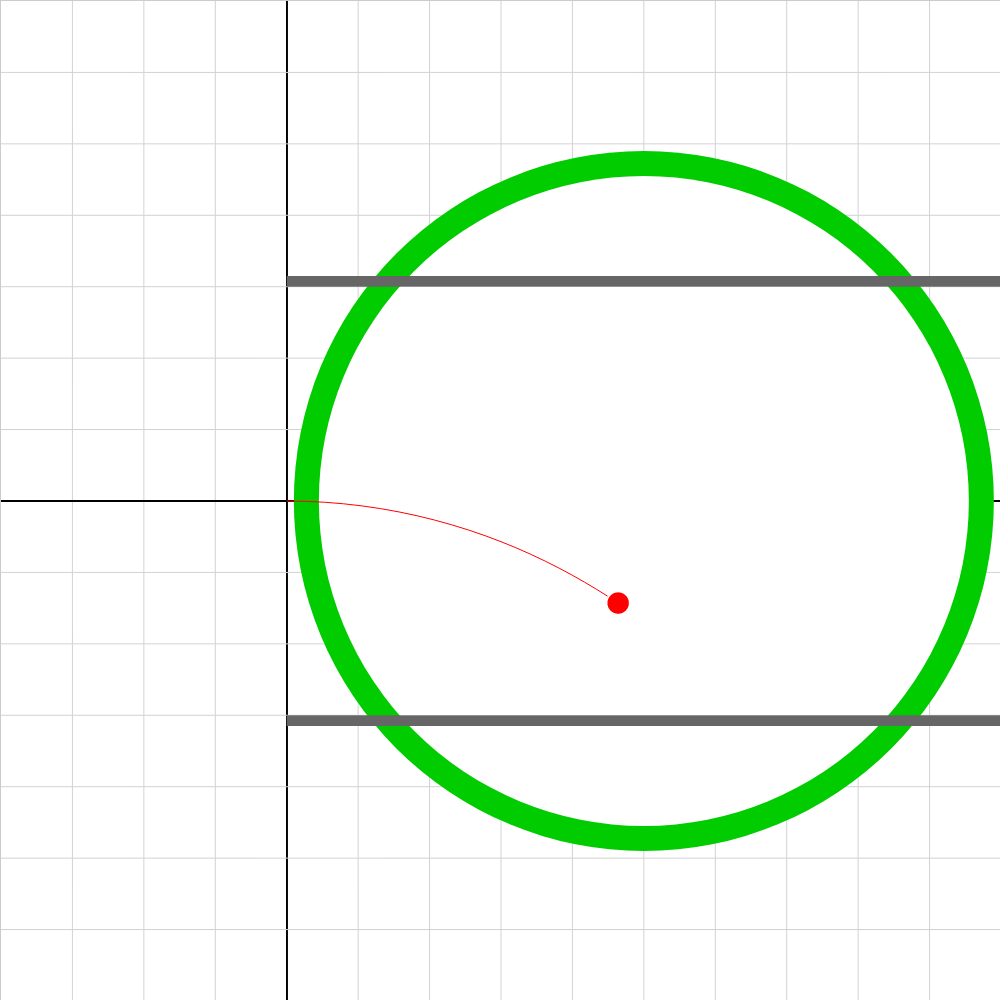
epotential-01c.iwp
At t = 0 , a charged particle is released in a uniform electric field at the given position. The electric field is produced by 2 charged plates on opposite sides of the screen, 20 cm apart. The electric field is represented by the green lines and the equipotentials by the gray lines. The direction of the electric force on the particle is indicated. Charge in units of e (1 e = 1.6E-19 C) is given as an input. Mass in units of u (1 u = 1.66E-27 kg) is given as an output. The potential difference may be reversed by making the potential of the left plate negative. The potential at the current position of the particle is shown as an output. The bar graphs in the yellow window show the electrical potential energy and the work done by the electric field on the particle as it moves.
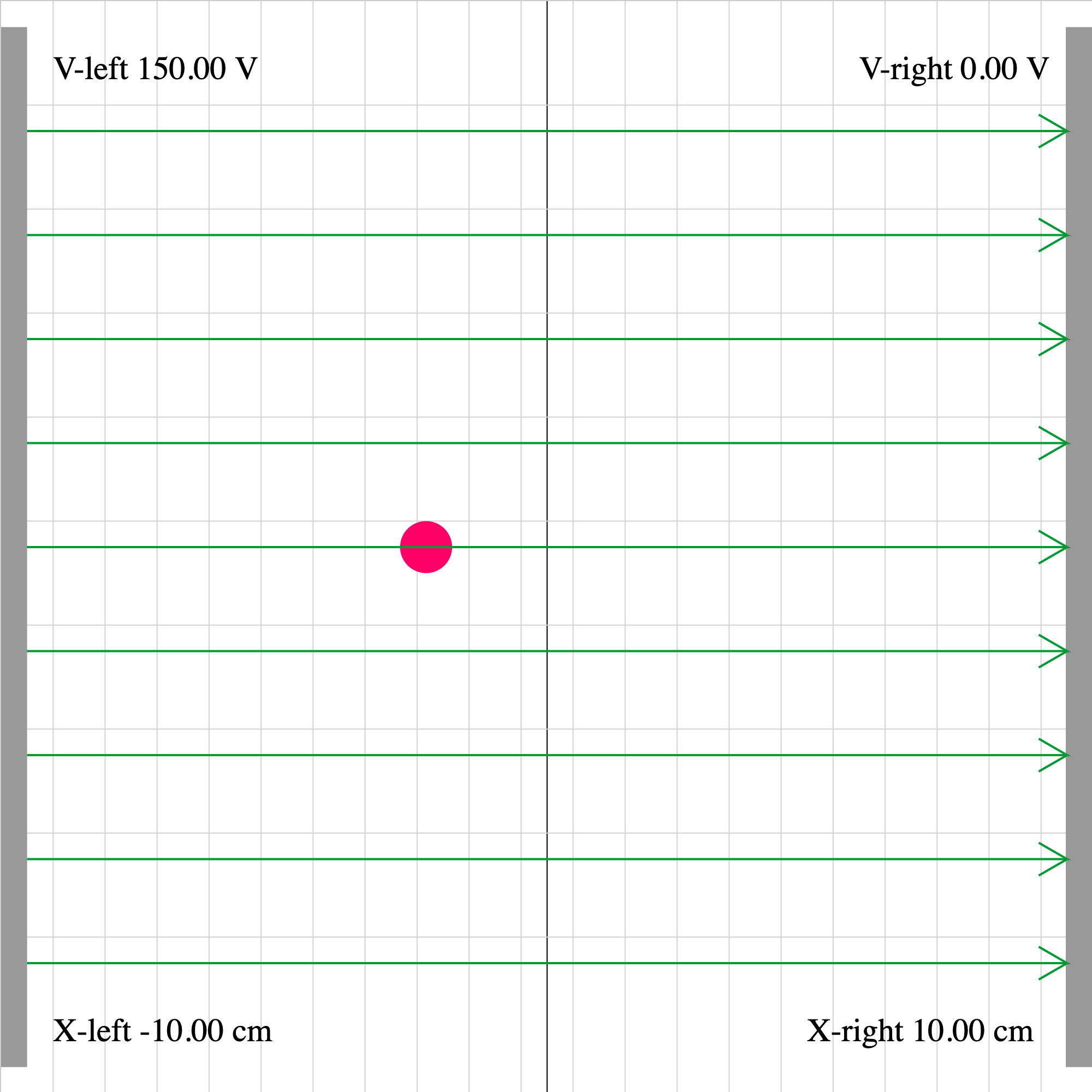
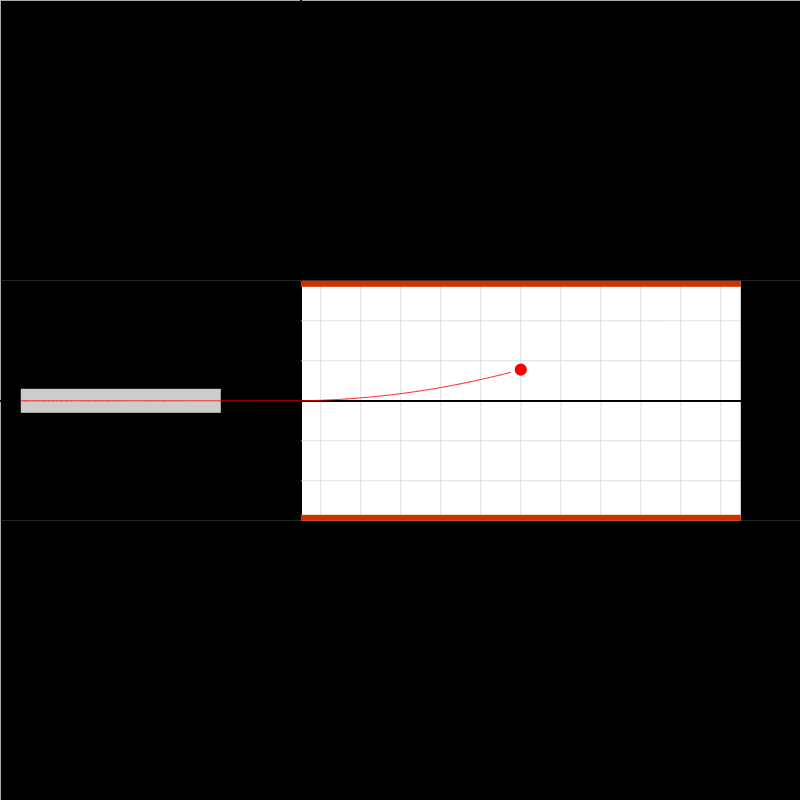
epotential-02d.iwp
A charged particle is acted on by two forces: 1) the force of the electric field set up between the plates, and 2) an external force. The position and velocity of the charge are given as outputs. Determine the direction and magnitude of the external force.
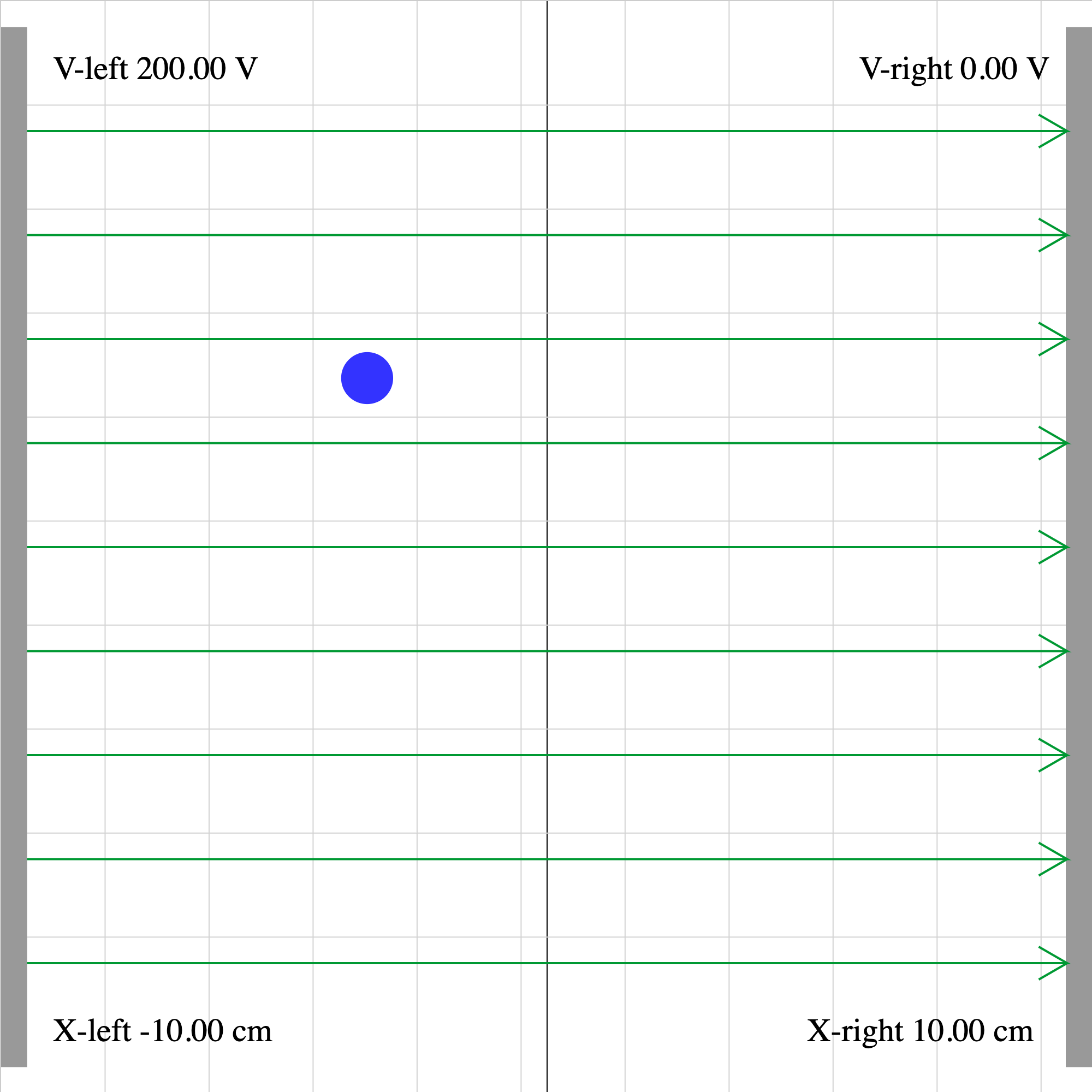
epotential-02e.iwp
A charged particle enters a uniform electric field at the bottom of the screen.
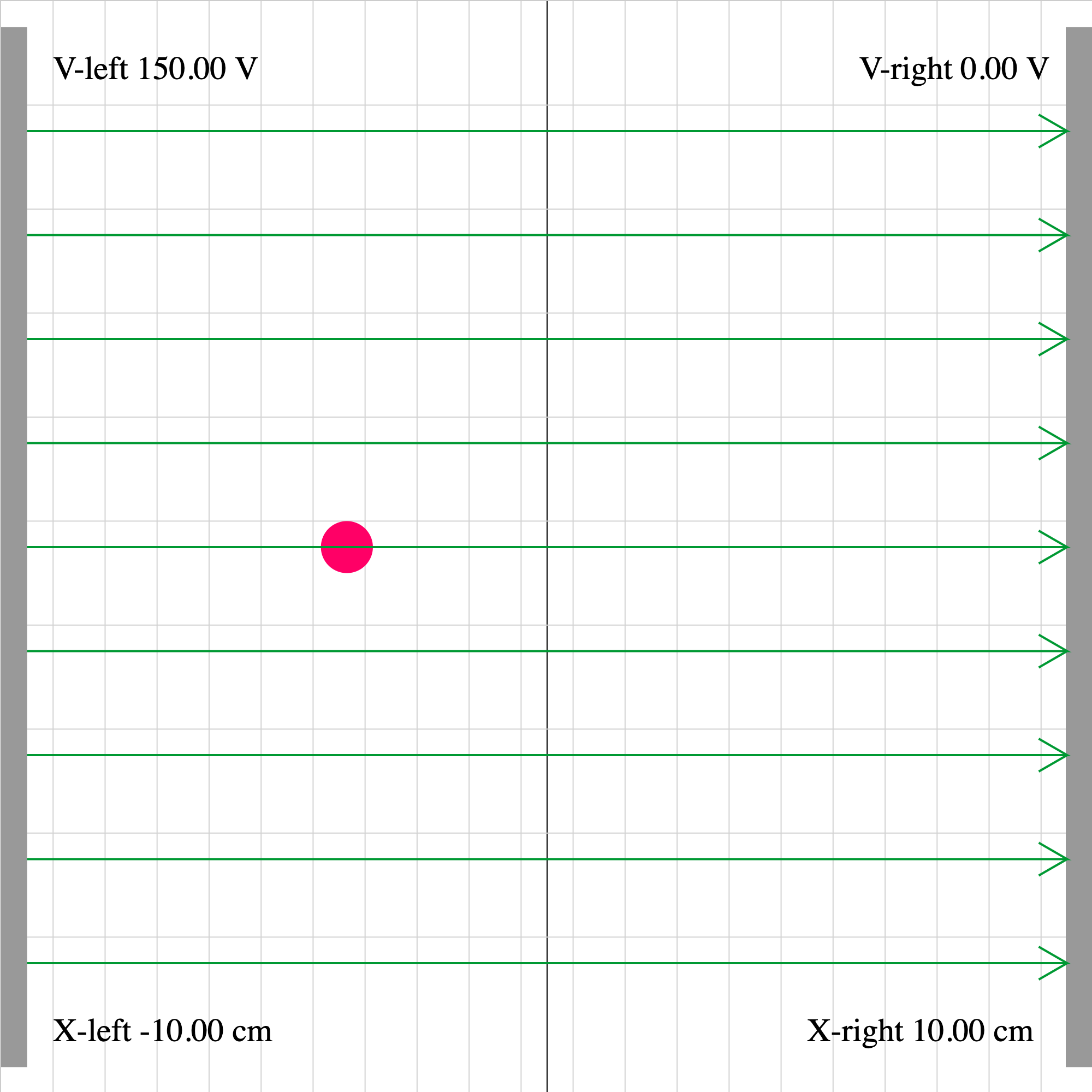
epotential-02f.iwp
A positive charge is initially moving to the left. How can you tell that there must be an external force acting on the particle?
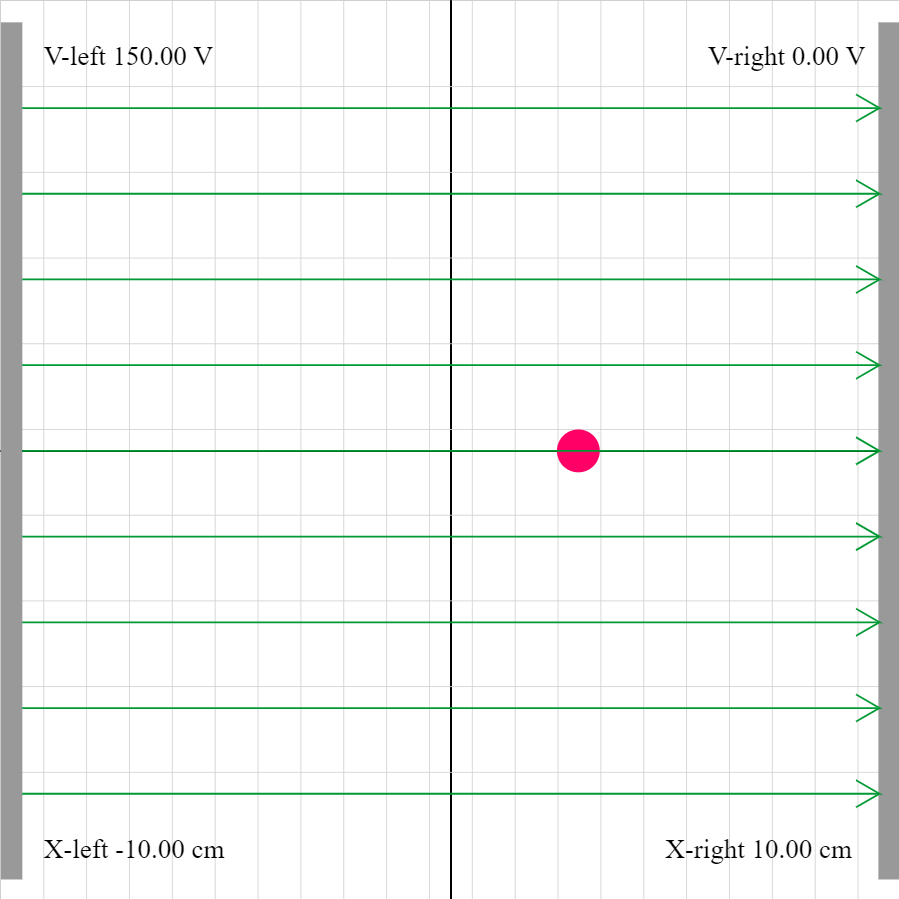
epotential-02j.iwp
A charged particle is acted on by two forces: 1) the force of the electric field set up between the plates, and 2) an external force. The position and velocity of the charge as well as the potential as a function of position are given as outputs. Determine the direction and magnitude of the external force.
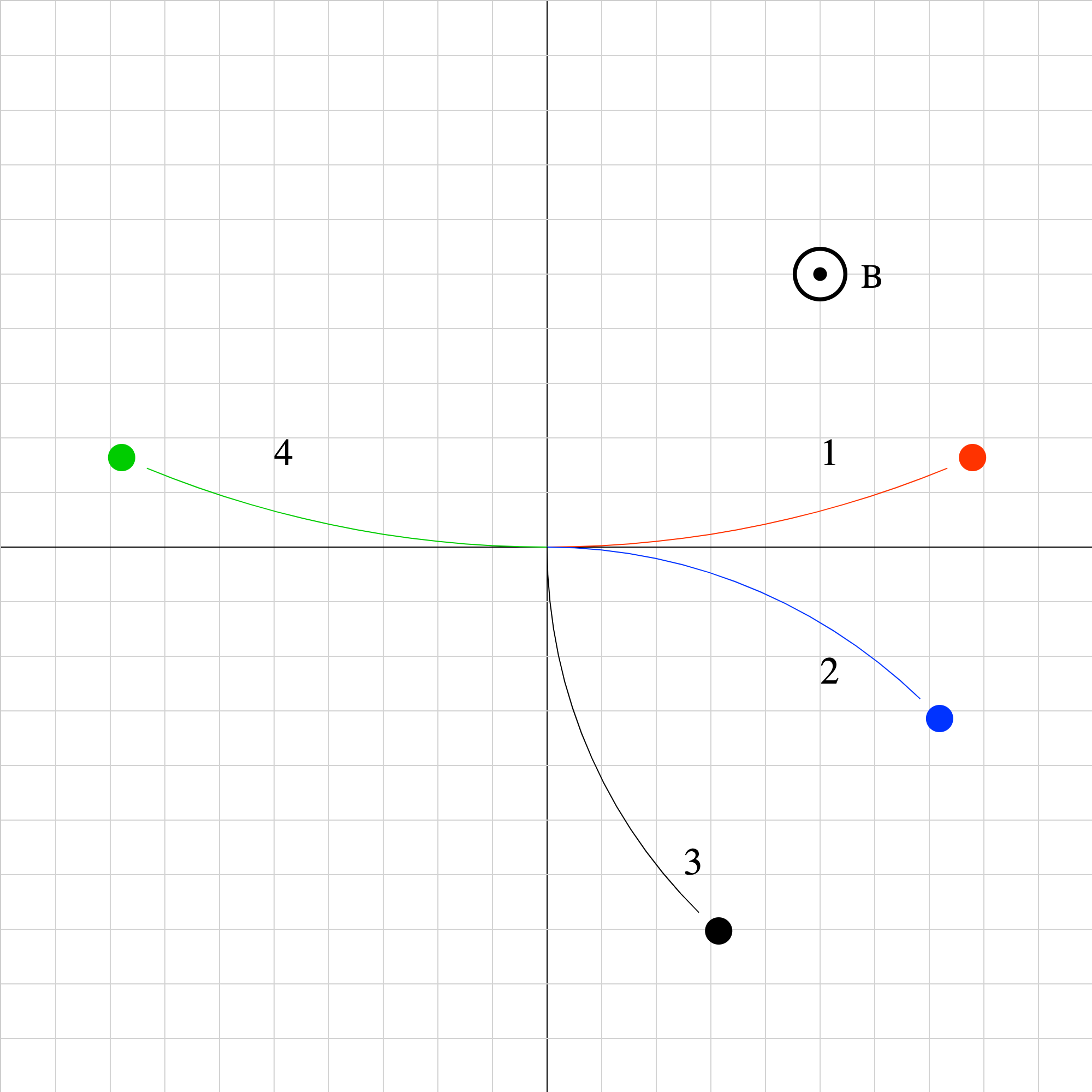
magforce-03.iwp
Four particles of equal mass and equal magnitudes of velocity have different charges. Run the applet to see how the particles move in a uniform magnetic field pointed perpendicularly out of the screen. Which particles are negative and which are positive?
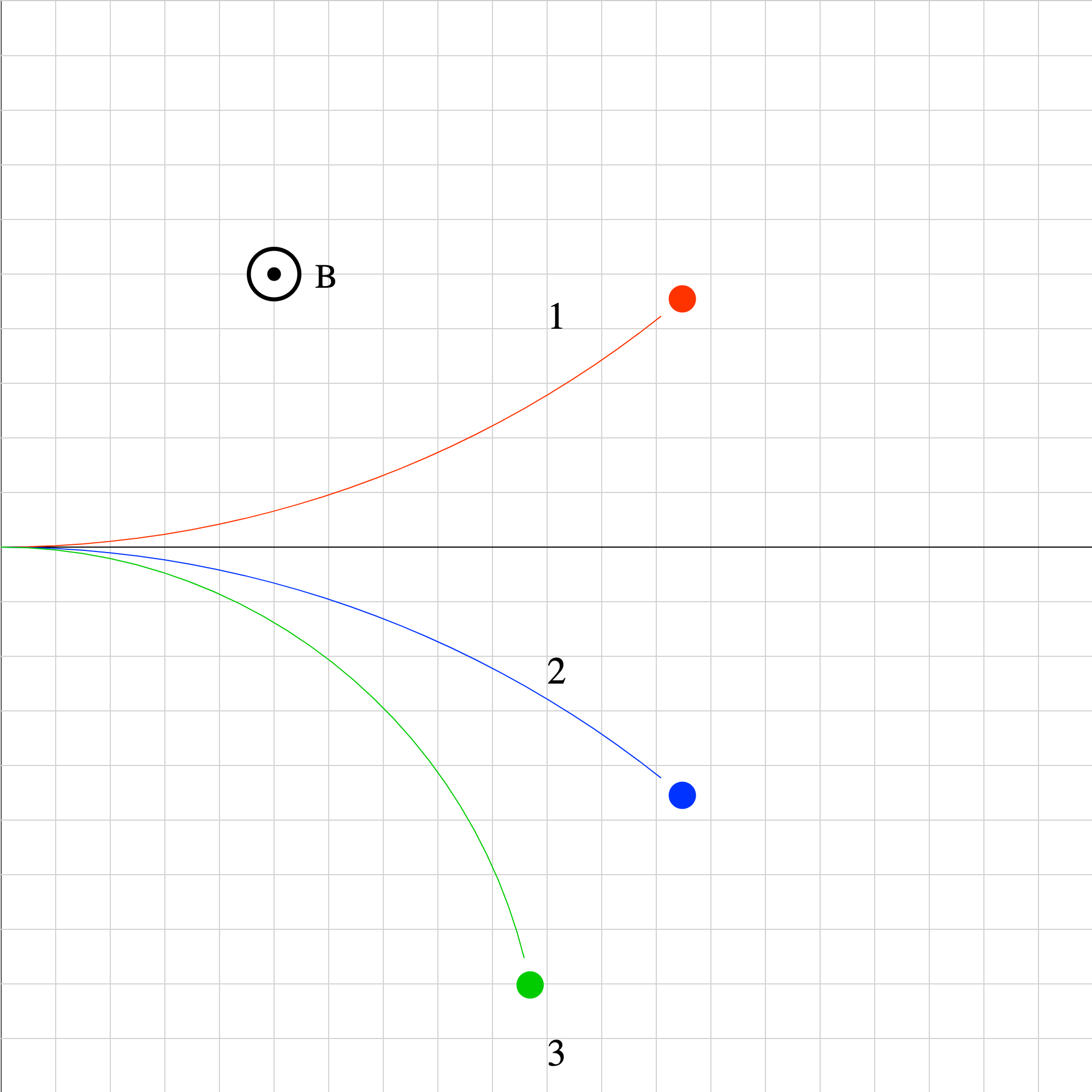
magforce-06.iwp
Three particles of equal mass and magnitude of velocity move in a uniform magnetic field pointed perpendicularly out of the screen. Rank the particles in increasing order according to the magnitude of their charge.
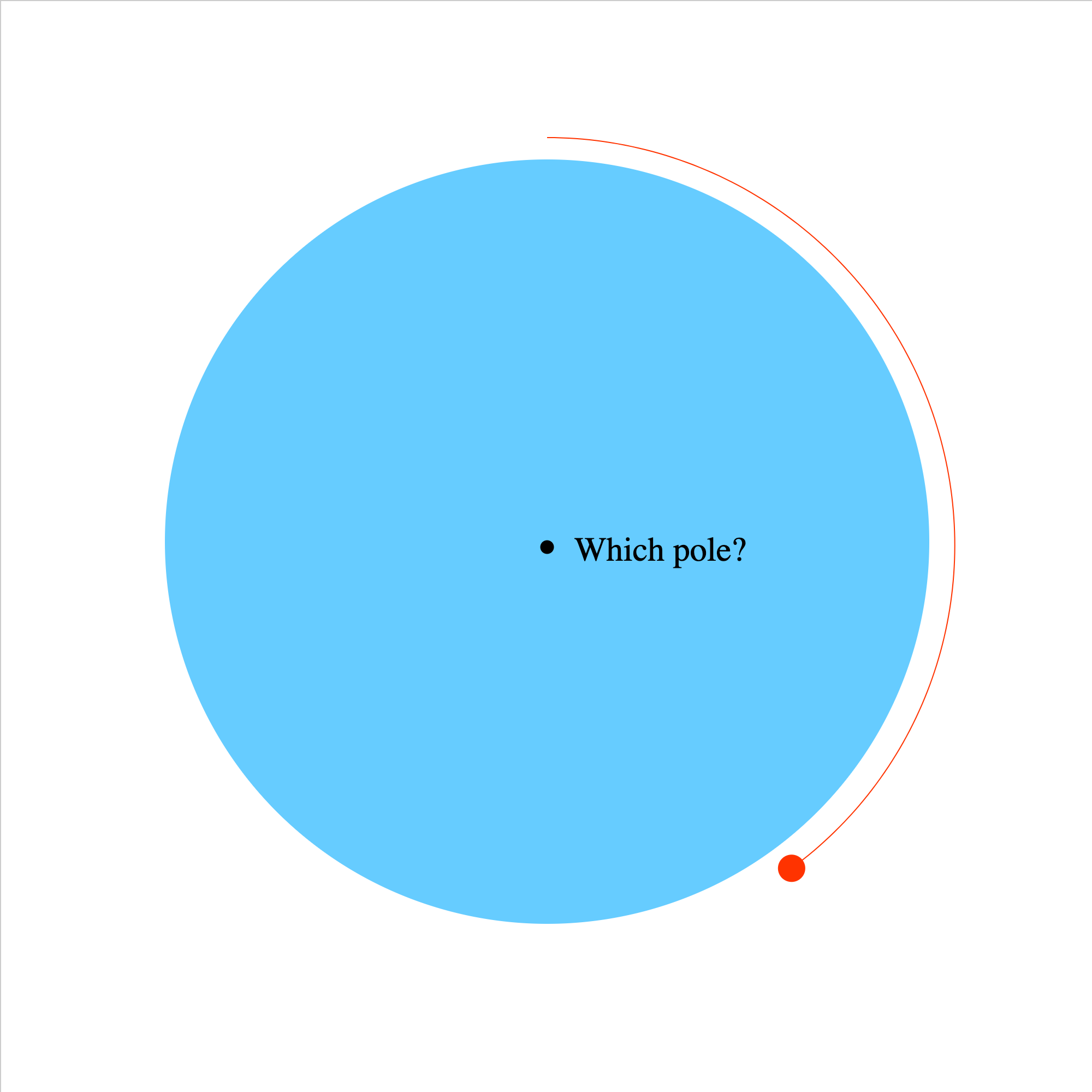
magforce-08.iwp
The view is that of an observer in space looking down on one of the poles of the Earth. An electron orbits the Earth at the equator under the influence of the magnetic force due to the Earth's magnetic field. The gravitational force on the electron can be ignored in comparison to the magnetic force. Which pole, magnetic north or south, is directly below and nearest the observer?
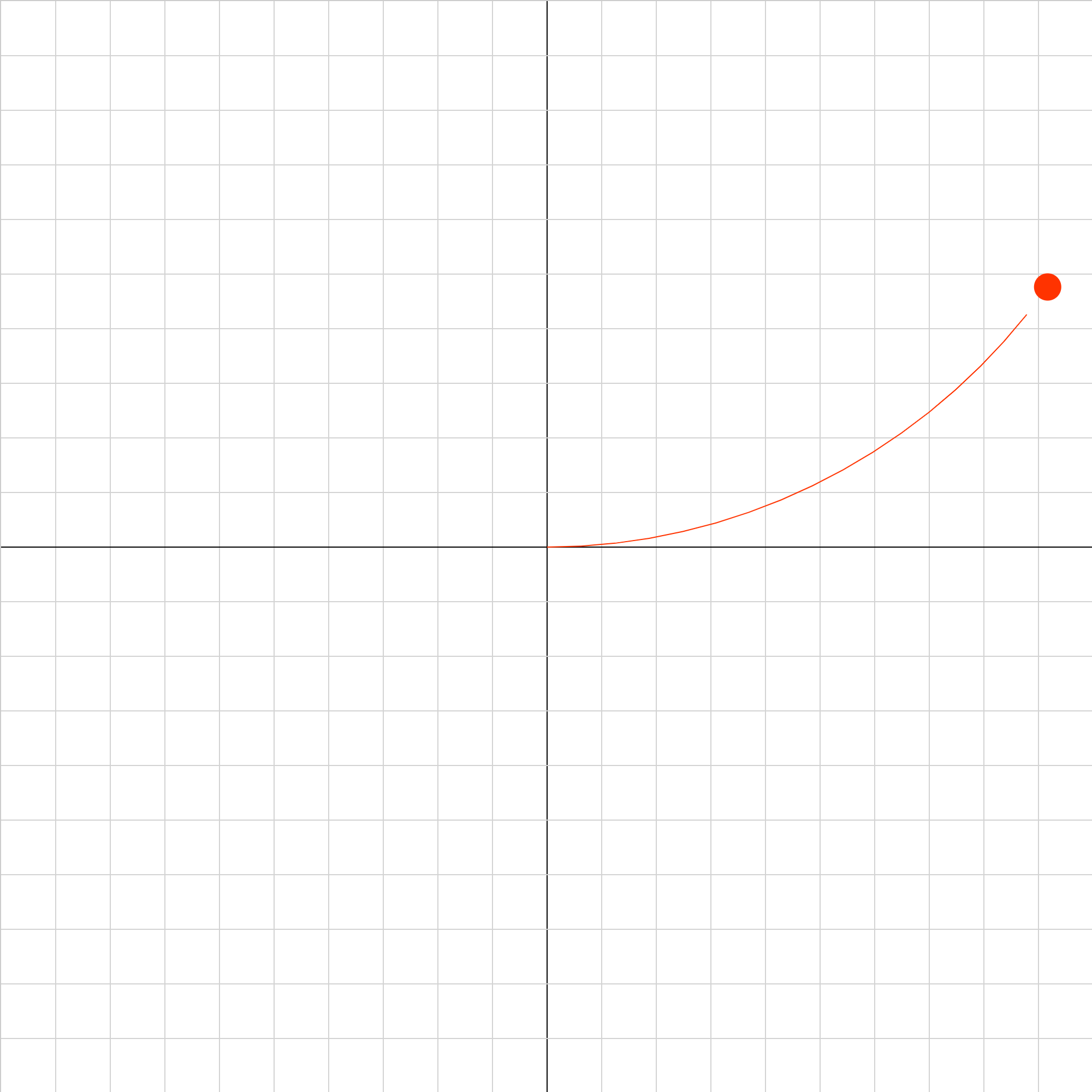
magforce-09.iwp
An electron moves under the influence of a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicularly outward from the screen. What must the direction and magnitude of a uniform electric field be such that the net force on the electron is 0 at the origin?
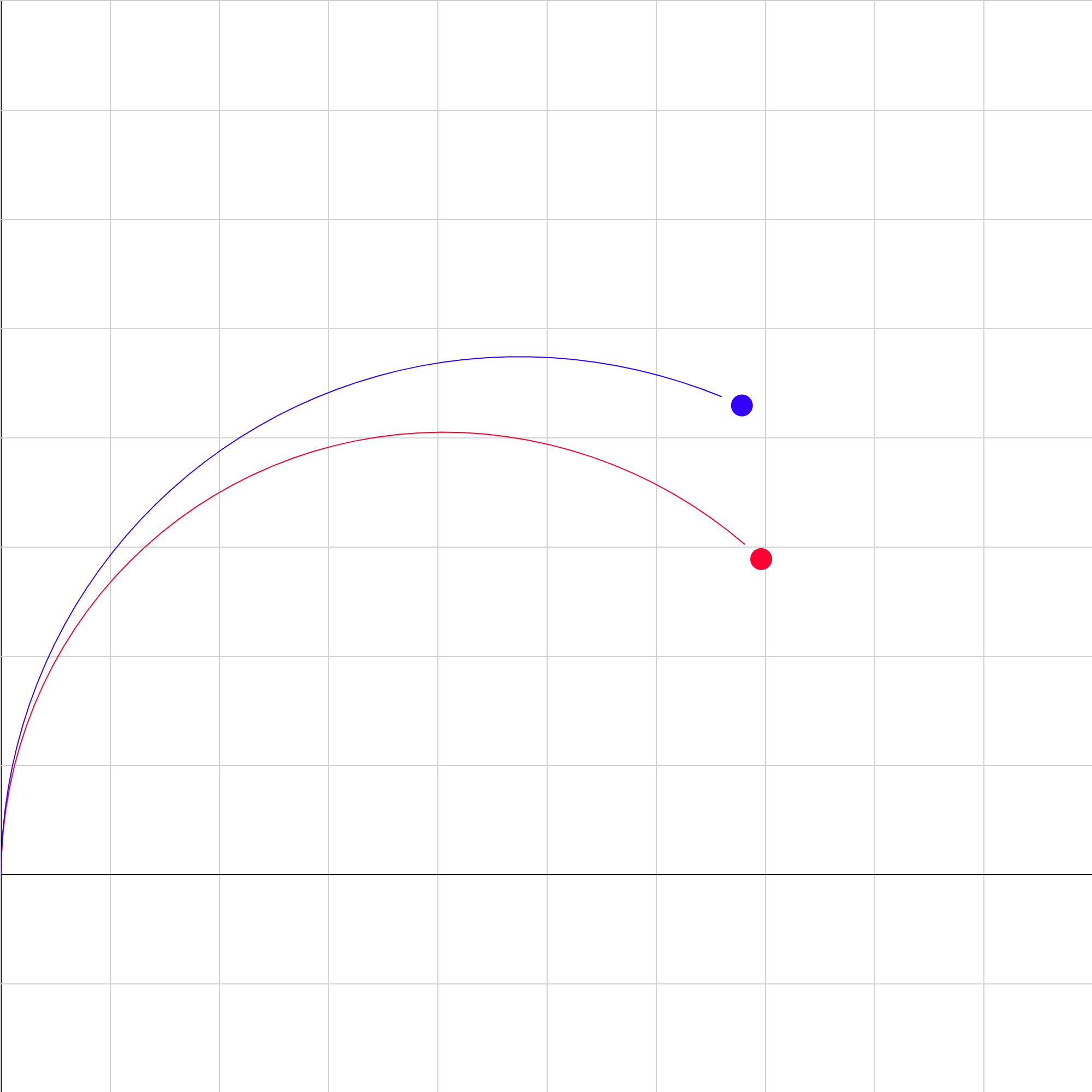
mass-spec.iwp
Two singly-ionized isotopes of the same element are injected at the same velocity into a region of uniform magnetic field pointing out of the screen. (There is no field below the x-axis). Determine the ratio of the masses of the isotopes.
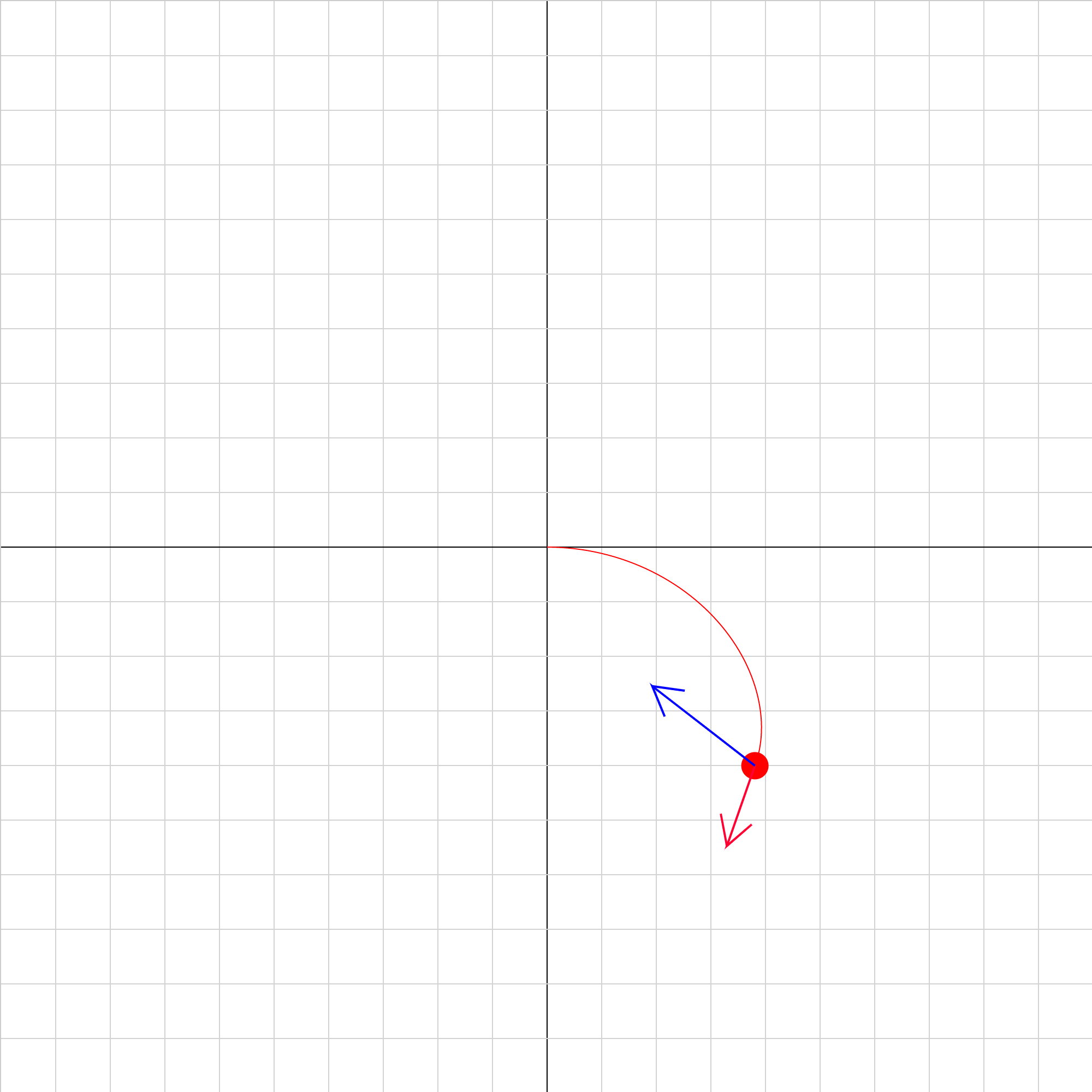
velocity-selector-02.iwp
A charged particle moves under the influence of an electric field oriented along the y-axis and a magnetic field oriented along the z-axis. Sign conventions: positive E is +y (toward top of screen) positive B is +z (outward from screen) Vectors: red = velocity blue = acceleration